Our lives are being lived through the use of various tools of AI. Artificial Intelligence has evolved from a visionary idea to a vital component of modern life. From Turing’s basic theory to today’s emerging era, AI has taken the way we live, work, and think to another level.
In this article, we will learn about the untold history of Artificial Intelligence. How Artificial Intelligence originated, how AI has evolved, and what role Artificial Intelligence plays in today’s sophisticated systems.
The Turing Era: The birth of an idea
The journey of artificial intelligence began with the famous British mathematician and computer scientist Sir Alan Turing.
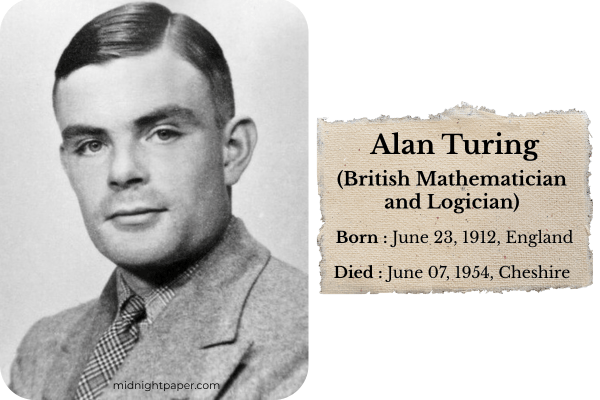
In 1950, he published his landmark paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”, in which he famously posed the question: “Can machines think?”
To answer this question, he proposed the Turing Test, which is often regarded as a milestone in machine intelligence. If a machine can conduct a conversation that is indistinguishable from human thought, then it can be considered intelligent. This idea laid the foundation for future Artificial Intelligence development.
1950s to 1960s: The Beginning of Artificial Intelligence Research
The term “Artificial Intelligence” was first used by John McCarthy in 1956 during the famous Dartmouth Conference. This event was the official birth of Artificial Intelligence.
Famous researchers such as Alan Newell, Herbert Simon, and Marvin Minsky began to explore machine learning, problem solving, and logical reasoning. They tried to delve deeper into the concept of Artificial Intelligence.

Logic Theorist:
Logic Theorist was created in 1956, one of the first such programs. Its main purpose was to be able to prove mathematical theorems.
ELIZA:
An early natural language processing program that mimicked human conversation for the first time.
MIT computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum created Eliza in 1966. Eliza is considered the first chatbot. It was designed to simulate therapy by reconstructing answers to users’ questions, which led to further conversations – also known as Rosarian reasoning.
Weizenbaum thought the simple nature of machine intelligence would prove the point. But many people began to think they were talking to a human professional. He explained in a research paper, “It was very difficult to convince some people that Eliza wasn’t human.”
These efforts, while rudimentary by today’s standards, are what made Aritficial Intelligence possible.
Shakey the Robot :
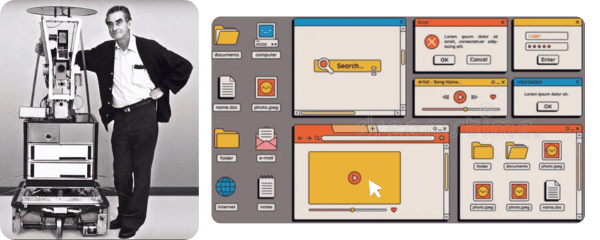
Shakey the Robot was a groundbreaking creation in the world of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence. It was developed by the Stanford Research Institute (SRI) in 1999.
Shakey was unique for its time. Its ability to perceive its environment, make decisions, and act on those decisions took on a whole new dimension. Shakey was equipped with a camera sensor and a set of wheels that allowed it to navigate its environment, detect obstacles, and perform tasks such as pushing boxes or opening doors. Shakey was laying the foundation for future AI planning systems.
Shakey marked a turning point in the integration of AI technologies such as advanced computer vision, natural language processing, and decision-making. It was the first robot to combine its capabilities on a mobile platform, influencing robotics research for decades and inspiring the design of more advanced systems.
Shakey’s legacy is still recognized, as it was inducted into the Robot Hall of Fame in 2004. It is currently on display at the Computer History Museum in California.
Seki helped lead the way to modern autonomous robots and AI-powered systems that are still in use today across various industries.
The 1970s: The First AI Winter
Despite initial excitement, Artificial Intelligence quickly outgrew its limitations. Early systems were unable to solve real-world problems. Funding was cut off due to expectations not being met, known as the first AI winter. Critics characterized Artificial Intelligence systems as unreliable.
In 1974, mathematician Sir James Lighthill published a critical report on academic AI research, claiming that researchers had largely overpromised and underdelivered on the potential intelligence of machines. His report led to a sharp reduction in funding.
Nonetheless, progress persisted in education, particularly in symbolic artificial intelligence and knowledge representation.
The 1980s: Expert Systems and a Revival
The 1980s saw a resurgence of artificial intelligence with the rise of expert systems. During this time, Artificial Intelligence was designed to simulate human decision-making using rule-based logic.
The most famous was XCON. These systems were commercially viable. However, these expert systems were very expensive to maintain and became brittle again as they grew in complexity. This led to a second AI winter in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
The 1990s: Machine Learning Takes the Lead
The 1990s saw a shift from these traditional rule-based systems to Machine Learning, where computers could learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed.
Learn More: Machine Learning vs Artificial Intelligence vs Deep Learning
Key developments:
IBM’s Deep Blue :
A chess-playing computer program.In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov at chess. This event was a major milestone in artificial intelligence, showing that machines are more capable than humans at complex tasks.
First driverless car :
Ernst Dickmans, a scientist working in Germany, invented the first self-driving car in 1986. Technically, it was a Mercedes van, equipped with a computer system and sensors to learn about the environment. The car could drive on the road without any controllers or passengers.
However, it was far from what we understand by AI-powered cars in the modern era. Dickmans’ car was the first step towards that AI dream.
This era focuses on pattern recognition, data mining, and practical applications in areas such as finance and healthcare.
AI growth: 2000-2019
With the explosion of the Internet and digital data, Artificial Intelligence has gained new momentum. Technologies such as search engines, recommendation systems, and voice recognition have emerged during this time.
KISMET :
Research on Kismet, a social robot, began in 1997. Its main task was to detect and imitate human emotions. This plan was implemented in 2000. In the MIT laboratory, led by Dr. Cynthia Breazeal, Kismet was programmed with sensors and a microphone to map “human emotional processes“. All of this enabled the robot to read and imitate emotions.
NASA Rovers :
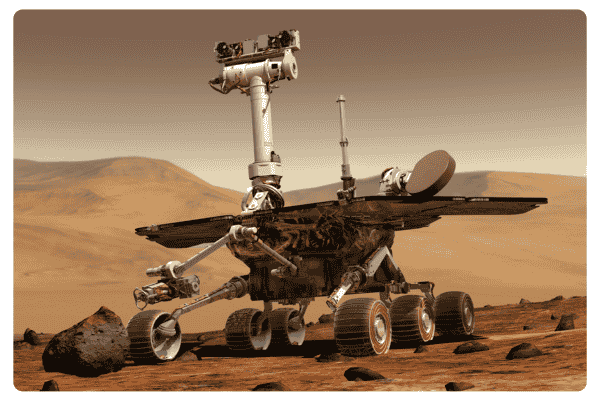
In 2004, Mars was orbiting much closer to Earth. NASA took advantage of this proximity by sending two rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, equipped with artificial intelligence. They were able to navigate the hard, rocky terrain of Mars and make decisions in real time without human assistance.
Siri and Alexa :
In 2011, Apple introduced a new feature called SIRI, a virtual assistant. Exactly three years later, Amazon released its virtual assistant called Alexa. Both could process natural language, such as understanding a question and attempting to answer it.
However, they still had limitations. Known as “command-and-control systems” SIRI and ALEXA are programmed to understand a limited list of questions, but these systems were unable to answer questions outside their scope.
Artificial Neural Networks :
Computer scientist Geoffrey Hinton began exploring the concept of neural networks in the 1970s while he was doing his PhD. Then, in 2012, when he and two of his graduate students showcased their research in the ImageNet competition, the tech industry saw the potential for neural networks.
Hinton’s work on neural networks and deep learning led AI to process large amounts of data, process natural language, and make accurate predictions. Hinton’s enthusiasm for such work led him to join Google in 2013. But in 2023, he resigned after becoming increasingly concerned about the dangers of artificial intelligence so that he could speak more freely about the dangers.
AlphaGO :
The ancient game of Go is considered straightforward to learn but incredibly difficult for any computer system to play, given the vast number of potential positions.
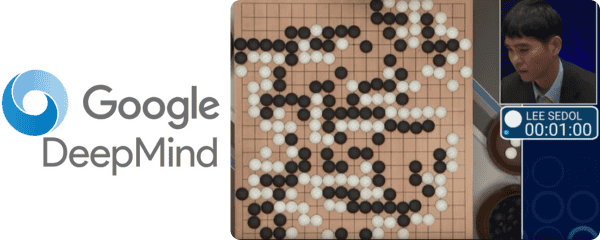
AlphaGO is a combination of neural networks and advanced search algorithms trained to play Go using a method called reinforcement learning. In 2016, AlphaGo, created by DeepMind, defeated the world champion Go player Lee Sedol, something that had long been thought impossible for a machine.
The 2020s: Generative AI and Ethical Concerns
With the emergence of Generative AI systems in the 2020s, AI took a different path in its development. These systems were capable of generating text, images, music, and even code. Since then, Google’s Gemini, OpenAI’s GPT model, and other large language models have pushed the boundaries of communication and creativity.
OpenAI and GPT-3 :
Artificial intelligence research firm OpenAI created a kind of generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) that became the foundation for their early language models GPT-1 and GPT-2, which were determined to be capable of producing unique text despite being trained using a large number of inputs.
Later, the Large Language Model (LLM) GPT-3 was released in 2020, creating a lot of buzz, indicating a breakthrough in AI. GPT-3 was trained on 175 billion parameters, which was much more than GPT-2, trained on 1.5 billion parameters.
MidJourney :
Launched in 2022 by independent research lab Midjourney. Midjourney is an AI-powered text-to-image model. It transforms natural language prompts into visually appealing and artistic images. Midjourney places a greater emphasis on aesthetic stylization.
Since its debut, Midjourney has undergone several updates, with version 6 offering improved coordination, detail, and faster accuracy.
The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence :
Today, we are seeing AI in almost every aspect of our lives. From the business sector, healthcare, and education to entertainment and manufacturing, Artificial Intelligence is being used everywhere.
However, with the advancement of multimodal AI, AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), and AI-human collaboration, the future looks both promising and complex.
Now that you’ve learned about the history of Artificial Intelligence, start building the skills you need to be part of the future by joining us.